Dynamic Chain-of-Thought (D-CoT) represents a departure from fixed, monolithic reasoning pipelines by introducing an adaptive mechanism that evaluates and refines intermediate steps in flight. Traditional chain-of-thought (CoT) systems generate a predetermined sequence of sub-steps regardless of their utility. In contrast, D-CoT continually assesses the relevance of each reasoning fragment, applying a partial-reward estimator alongside importance-based pruning and adaptive thresholding. This selective retention of high-value sub-steps preserves the interpretability of CoT explanations while eliminating extraneous computation, producing succinct yet transparent reasoning traces aligned to the complexity of the query.
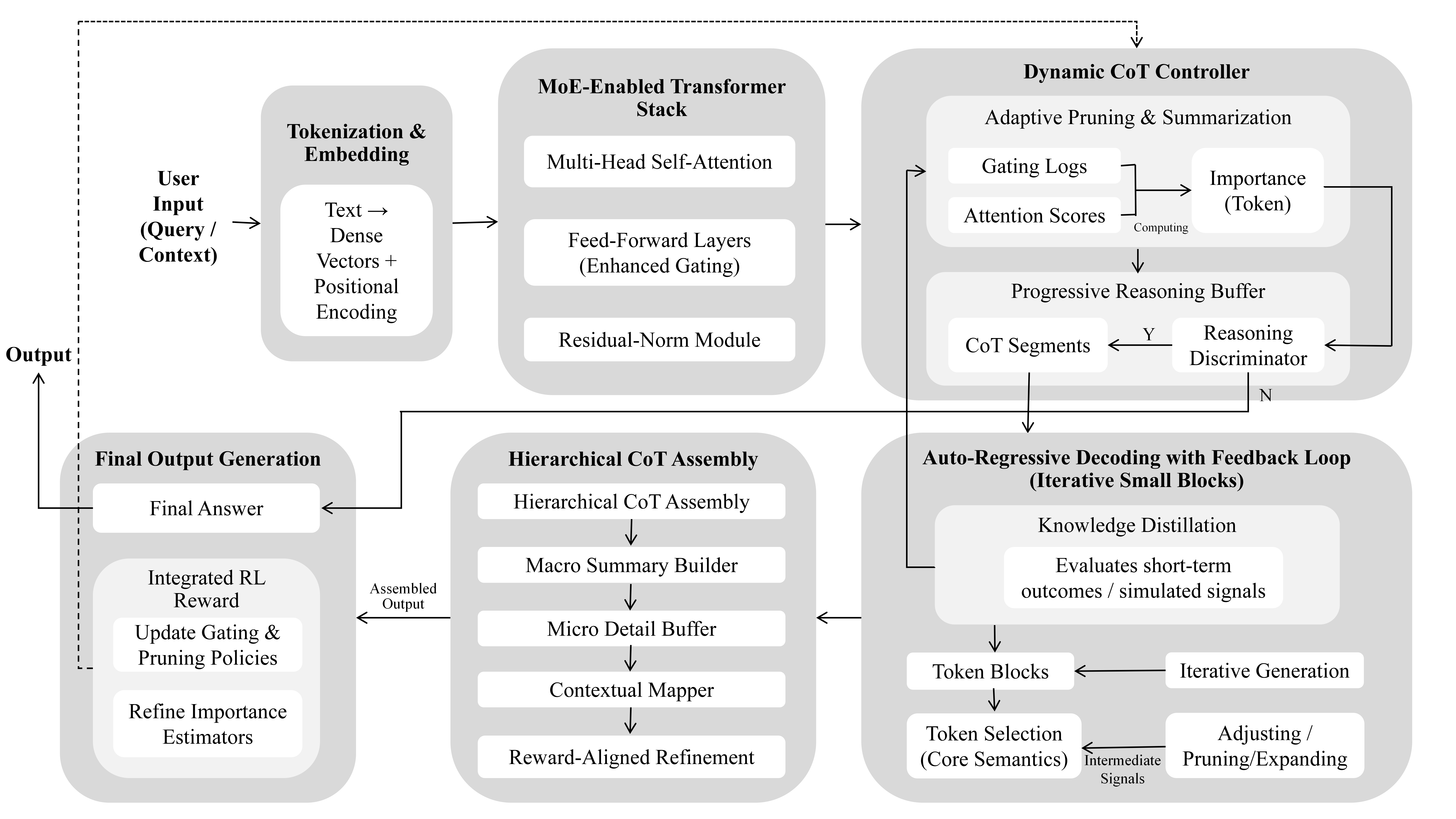
At the architectural level, D-CoT integrates a Hierarchical Adaptive Reward Optimization (HARO) module without altering the core pre-trained transformer. During decoding, every candidate step is scored according to a composite importance metric derived from reinforcement-learning signals and gating-influenced contribution measures. These scores are evaluated against a dynamic threshold that adapts to recent reward statistics. Steps that underperform are omitted, whereas those exceeding the threshold may undergo further elaboration. In parallel, a multi-scale progressive reasoning buffer aggregates retained fragments at both macro (summary) and micro (detail) levels. By fusing immediate reward feedback with importance-driven selection, D-CoT allocates computational resources to the most informative reasoning paths. The result is sub-second response delivery, on-demand control of reasoning depth, and a seamless interactive experience even under strict latency budgets.
In Veltraxor 1.0, the deployment of D-CoT has yielded marked performance gains along three axes: overall latency, reasoning-step count, and token throughput. When compared to a static CoT baseline (DeepSeek R1), Veltraxor reduced average reasoning time from 50–150 seconds to 40–120 seconds, lowered peak runtimes from 295 seconds to approximately 180 seconds, and compressed reasoning chains from up to eight steps down to three–six steps. Token consumption likewise shrank by 40–50 percent, dropping from spikes above 320 tokens to a steady 70–180-token range. These efficiencies translate directly into faster, more cost-effective interactions without compromising answer fidelity. D-CoT thus demonstrates its ability to satisfy the throughput demands of enterprise deployments while upholding rigorous compliance and resource constraints.